Publish at
Presentation
Our research program is aiming to identify genes, non-coding genomic alterations or post-transcriptomic modifications responsible for congenital malformations and answer important questions in clinics, biology and developmental genetics. We have a special interest for tissues derived from the neural crest (neurocristopathies), and ciliopathies.
The neural crest is a transitory embryonic structure that participates to the development of many structures. We have a long lasting interest on the development of the enteric nervous system and Hirschsprung disease, a model for complex oligogenic and sex-dependent inheritance. In collaboration with many reference centers for rare diseases on the Necker Hospital campus we also developed research projects on craniofacial anomalies (especially mandibulofacial dysostoses), syndromic deafness (including Waardenburg syndrome) and cardiac malformations through NGS, in vitro and in vivo analysis. For each project, our models include iPS cells and their differentiation towards lineages of interest and/or development of animal models (zebrafish and mouse).
Ciliopathies are a fast growing group of diseases that are the consequence of an abnormal genesis or functioning of the motile and/or primary cilia. Our work on ciliopathies contributes to the understanding of primary cilium formation and links extreme lethal phenotypes with viable syndromes. A recent focus has been made on cerebral defects associated to primary cilia dysfunction that will be investigated by 2D and 3D cell-based models of neocortical development (cerebral organoids) generated from patient-derived IPS cells.
Team
Resources & publications
-
 2020Journal (source)Am. J. Hum. Genet.
2020Journal (source)Am. J. Hum. Genet.Bi-allelic Variations of SMO in Humans Cause a Broad Spectrum of Developmenta...
-
 2019Journal (source)Hum. Mol. Genet.
2019Journal (source)Hum. Mol. Genet.PAICS deficiency, a new defect of de novo purine synthesis resulting in multi...
-
 2019Journal (source)Brain
2019Journal (source)BrainMN1 C-terminal truncation syndrome is a novel neurodevelopmental and craniofa...
-
 2019Journal (source)Biol. Cell
2019Journal (source)Biol. CellCilia in hereditary cerebral anomalies.
-
 2018Journal (source)Am. J. Hum. Genet.
2018Journal (source)Am. J. Hum. Genet.Mutations in TUBB4B Cause a Distinctive Sensorineural Disease.
-
 2017Journal (source)Am. J. Hum. Genet.
2017Journal (source)Am. J. Hum. Genet.FDXR Mutations Cause Sensorial Neuropathies and Expand the Spectrum of Mitoch...
-
 2017Journal (source)Nat. Genet.
2017Journal (source)Nat. Genet.De novo mutations in SMCHD1 cause Bosma arhinia microphthalmia syndrome and a...
-
 2017Journal (source)Gastroenterology
2017Journal (source)GastroenterologyDifferentiation of Mouse Enteric Nervous System Progenitor Cells Is Controlle...
-
 2017Journal (source)Dev. Biol.
2017Journal (source)Dev. Biol.Mouse models of Hirschsprung disease and other developmental disorders of the...
-
 2017Journal (source)Am. J. Hum. Genet.
2017Journal (source)Am. J. Hum. Genet.Biallelic PPA2 Mutations Cause Sudden Unexpected Cardiac Arrest in Infancy.
-
 2016Journal (source)Hum. Mol. Genet.
2016Journal (source)Hum. Mol. Genet.Subnuclear re-localization of SOX10 and p54NRB correlates with a unique neuro...
-
 2016Journal (source)Nat. Genet.
2016Journal (source)Nat. Genet.MMP21 is mutated in human heterotaxy and is required for normal left-right as...
-
 2014Journal (source)Am. J. Hum. Genet.
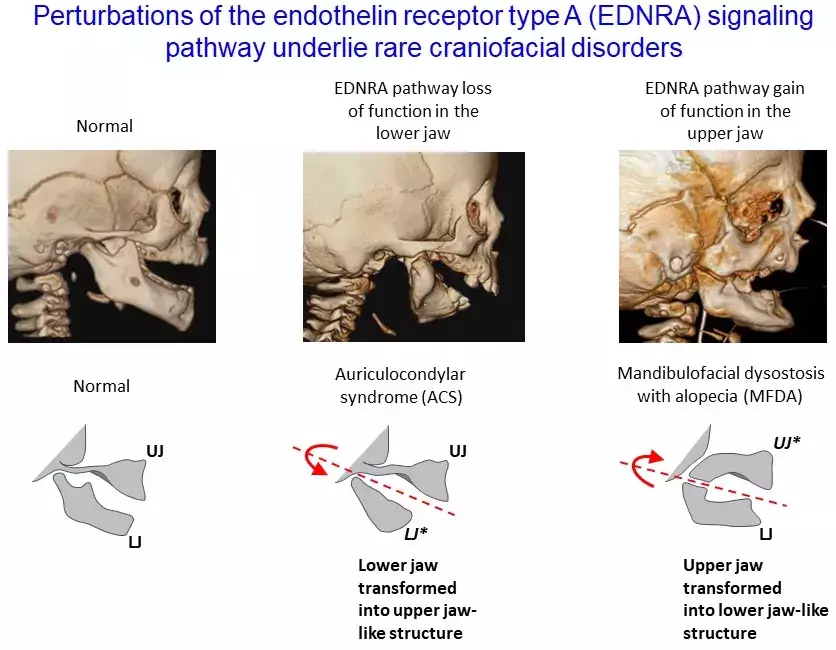
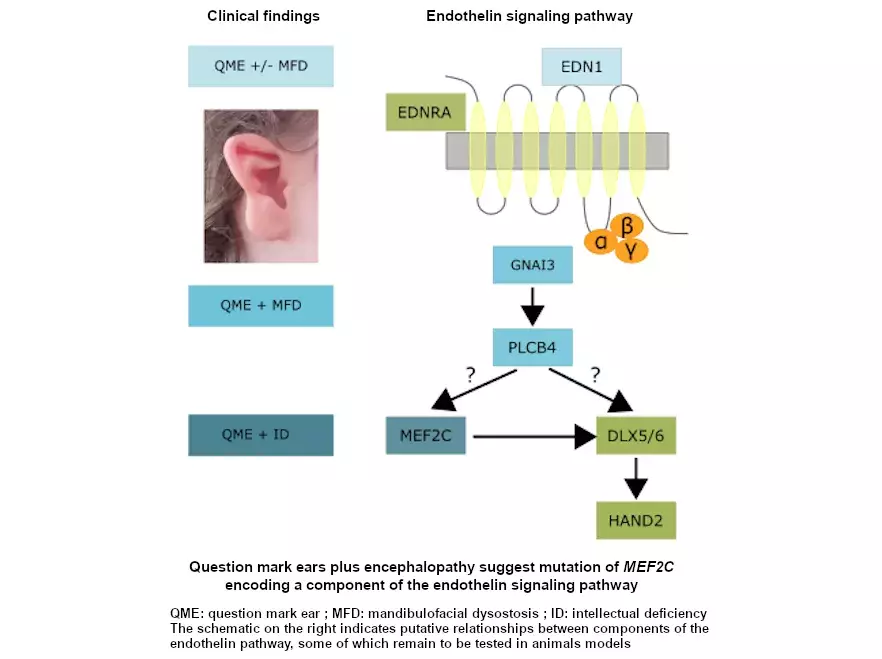
2014Journal (source)Am. J. Hum. Genet.Mutations in endothelin 1 cause recessive auriculocondylar syndrome and domin...
-
 2015Journal (source)Am. J. Hum. Genet.
2015Journal (source)Am. J. Hum. Genet.Mutations in the endothelin receptor type A cause mandibulofacial dysostosis ...
-
 2013Journal (source)J. Med. Genet.
2013Journal (source)J. Med. Genet.EFTUD2 haploinsufficiency leads to syndromic oesophageal atresia.
-
 2011Journal (source)Nat. Genet.
2011Journal (source)Nat. Genet.Germline deletion of the miR-17∼92 cluster causes skeletal and growth defects...
-
 2009Journal (source)Nat. Genet.
2009Journal (source)Nat. Genet.Highly conserved non-coding elements on either side of SOX9 associated with P...
-
 2008Journal (source)Nature
2008Journal (source)NatureSomatic and germline activating mutations of the ALK kinase receptor in neuro...
Research: a scientific adventure
Our goal: to better understand genetic diseases to better treat them.